
Geo Information
Aerial Surveys
Aerial Survey has been done since 1952 to provide geo spatial data for a wide range of applications. Aerial photography is the taking of photographs of the terrain from air. The term usually refers to images in which the camera is not supported by a ground-based structure. Cameras may be hand held or mounted, and photographs may be taken by a photographer, triggered remotely or triggered automatically. Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, balloons, rockets, kites. Aircraft are used as platform for a wide range of air borne remote sensing system. Aerial photographs were the first form of remote sensing imagery, and they remain the most widely used images today.
It is the oldest, yet most commonly applied remote sensing technique. Photogrammetry is the science and technique of making measurements from photographs or image data.
At present, Topographic maps produced by the Survey Department are based on Aerial Surveys other than the new 50k series. Large scale Aerial photographs also provide the accurate data for many engineering projects as well as source of information for specialist such as Foresters, Geologists and Urban Planners etc.
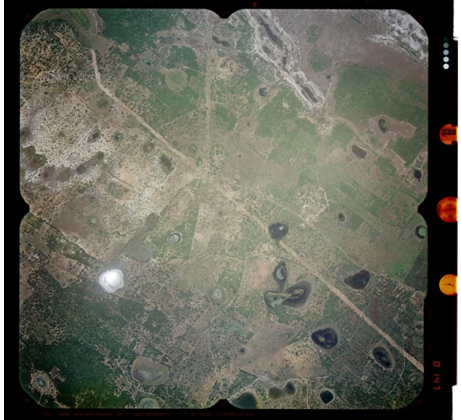
Prior to aerial photographs better to consider flying charts which is assist to navigation of air craft and aerial photography. Using these flying charts pilots are able to determine their position, scale altitude and best route of destinations etc. In most mapping applications vertical aerial photography is required. Vertical aerial photography is produced with a camera mounted in the floor of an aircraft. The resulting image is rather similar to a map and has a scale that is approximately constant throughout the image and area covered in single photograph is 23cmx23cm with following marginal information,
-
Photo Number and year
-
Line and Roll number
-
Scale code and 50K sheet number
-
Watch, altimeter and level bubble
-
Fuducial marks
According to the project requirements following factors to be considered before taking aerial photographs. Namely, project area, photo scale, direction of strips, coordinate system, film type and camera type etc.
In addition, vertical aerial photographs are also taken in stereo, manner in which successive photos have a degree of overlap (Forward overlap is 60% and lateral overlap is 25%) to enable stereo interpretation and stereo measurements like contours and spot heights.
Processed and annotated photographs are handed over to the photogrammetric unit to extract vector data according to the predetermined project scale. Final output will be the scaled vector data set in dgn format.
In addition to that Department has capability of produce Color/BW ortho Images or image maps as a result of having color aerial photographs in year 2010/2011 for Northern province covering 9000 sq.km under the JICA North Mapping Project. Data extraction of 1:10,000 scale for those areas were completed in 2013.
Analogue air photographs and scanned air photographs are being used to collect terrain information. Stereo Compilation of the data is done by digital photogrammetric workstations and analytical photogrammetric plotters. High resolution photo scanners are being used to convert the analog air photos to digital form with resolution varies from 508µ(50dpi) to 2µ(12,700dpi). It provides facility to produce high quality scanned aerial photographs with short time period.
Available digital data for users:
-
1:10,000 topographic data (digitized 10k maps and map manuscript, digital stereo compiled data, 2D data extracted from high resolution satellite images) to cover 80% of Sri Lanka
-
1:5000 covered only 24 town areas
-
1:2000 covered only Colombo and suburbs